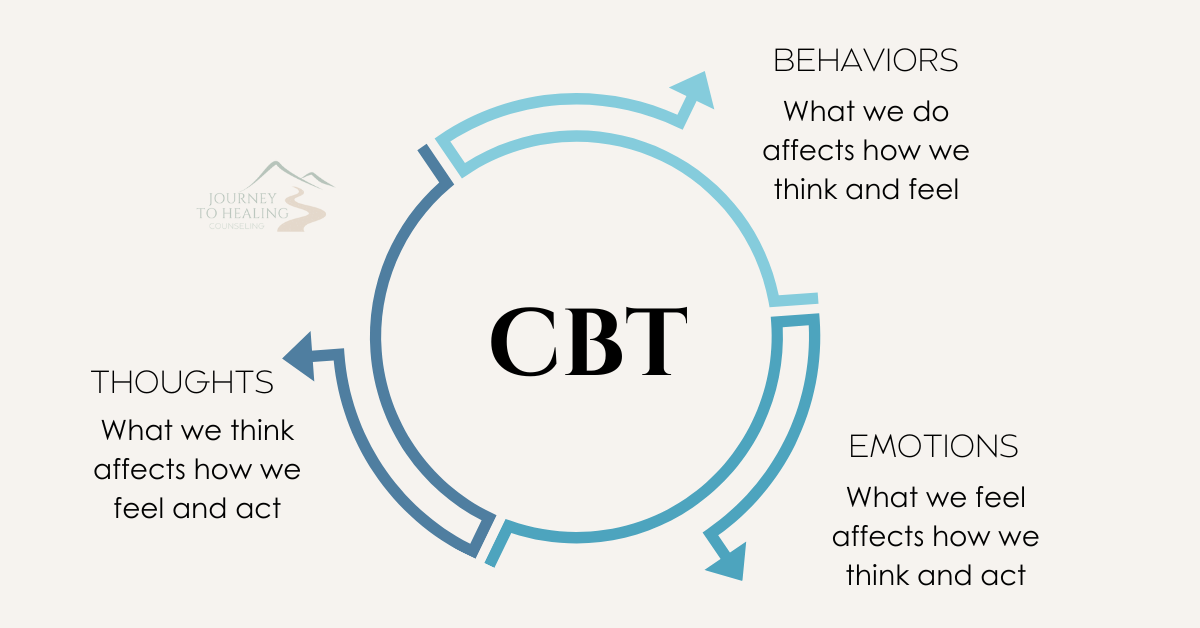
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely used and evidence-based form of psychotherapy that focuses on the connections between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It is based on the idea that our thoughts influence our emotions and behaviors and that changing maladaptive thought patterns can lead to improvements in mood and behavior.
Key principles of CBT include:
- Cognitive restructuring: CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative or irrational thoughts and beliefs that contribute to emotional distress or problematic behaviors. By questioning the accuracy and validity of these thoughts, individuals can develop more balanced and realistic ways of thinking.
- Behavioral activation: CBT encourages individuals to engage in activities that bring them a sense of pleasure or accomplishment, even when they may not feel like doing so. By increasing participation in rewarding activities, individuals can counteract feelings of depression or lethargy.
- Skills building: CBT teaches practical skills and techniques to help individuals cope with stress, manage emotions, and solve problems more effectively. These skills may include relaxation techniques, assertiveness training, communication skills, and stress management strategies.
- Exposure therapy: In cases of anxiety disorders, phobias, or trauma-related conditions, CBT may incorporate exposure techniques to help individuals gradually confront and overcome their fears or traumatic memories in a controlled and supportive environment.
- Homework assignments: CBT often involves homework assignments between therapy sessions, where individuals practice applying the skills and techniques they’ve learned in therapy to real-life situations. This helps reinforce learning and promotes the generalization of skills to everyday life.
CBT is typically structured and goal-oriented, with a focus on identifying specific problems and developing targeted interventions to address them. It is usually delivered in a time-limited format, with a set number of sessions determined collaboratively between the therapist and client.
CBT has been extensively researched and has been found to be effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), eating disorders, and substance use disorders. It can be delivered in individual therapy, group therapy, or self-help formats, and it is often integrated with other therapeutic approaches depending on the needs of the individual.