Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) that was originally developed by psychologist Marsha M. Linehan in the late 1980s. It was initially designed to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD) but has since been adapted and proven effective for various other mental health conditions.
DBT combines elements of cognitive-behavioral techniques with concepts of mindfulness and acceptance. It is based on the dialectical philosophy, which suggests that opposing forces can be synthesized to create a greater understanding or resolution. In therapy, this means accepting a client for who they are while recognizing that change is necessary for growth and healing.
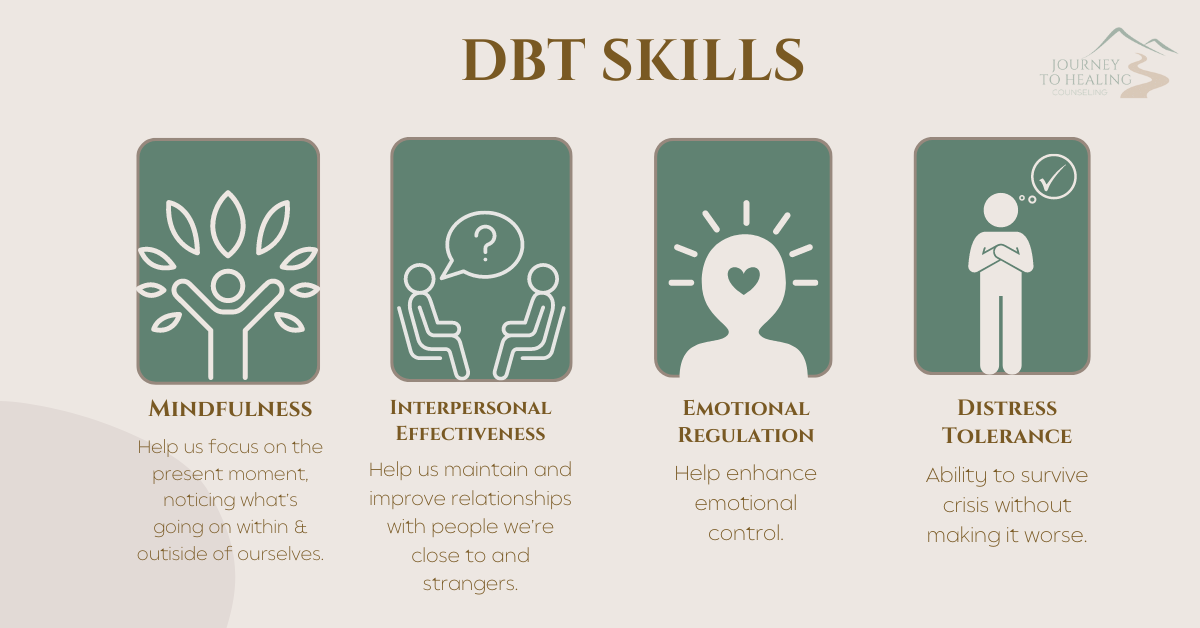
Key components of DBT include:
- Mindfulness: DBT emphasizes the practice of mindfulness, which involves being present in the moment without judgment. Clients learn to observe their thoughts, emotions, and sensations without reacting impulsively or engaging in harmful behaviors.
- Distress tolerance: DBT teaches clients skills to tolerate and cope with distressing emotions without resorting to self-destructive behaviors such as self-harm or substance abuse. These skills include distraction techniques, self-soothing activities, and improving the ability to tolerate emotional pain.
- Emotion regulation: Clients learn strategies to effectively identify, understand, and regulate their emotions. This involves learning to label emotions accurately, identify triggers, and develop healthy ways of coping with intense feelings.
- Interpersonal effectiveness: DBT helps clients develop assertiveness skills, set boundaries, and communicate effectively in their relationships. Clients learn how to navigate interpersonal conflicts, negotiate needs, and build healthier relationships.
- Dialectics: DBT encourages clients and therapists to embrace dialectical thinking, which involves recognizing and reconciling contradictions. This can include accepting oneself while also striving for change, balancing validation and accountability, and finding synthesis between opposing perspectives.
DBT is typically delivered in both individual therapy sessions and group skills training sessions. It has been shown to be effective not only for borderline personality disorder but also for other conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, substance use disorders, eating disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).